In this article, I will explain, how to Improve Website Response using Traffic Manager. Use Traffic Manager to create a highly responsive website by directing user traffic to the website with the lowest latency. Generally, the datacenter with the minimum latency is the one that is closest to the geographic distance.
In this article, you learn how to:
Create two virtual network
Create 2 VMs running a basic website on (IIS)
Configure DNS name for the VMs (running IIS)
Create two tests VMs to view Traffic Manager in action
Create a “Traffic Manager profile” for improved website performance
Add VM (Instance) endpoints to the Traffic Manager profile
View Traffic Manager in action
Prerequisites
In the interest of see the Traffic Manager in action, this article requires that you deploy the following:
2 instances (VMs) of basic websites running in different Azure regions – (East US and West Europe).
2 test VMs for testing the Traffic Manager – 1st VM in West Europe and the 2nd VM in East US. The test VM (Instance) is used to represent how Traffic Manager Routes user traffic to the website that is running in the same region as it provides the lowest latency.
Improve Website Response using Traffic Manager
Sign in to the Microsoft Azure portal
Create a virtual network
1- In the search bar type (virtual networks) to find or from the Azure portal menu and then select virtual networks.
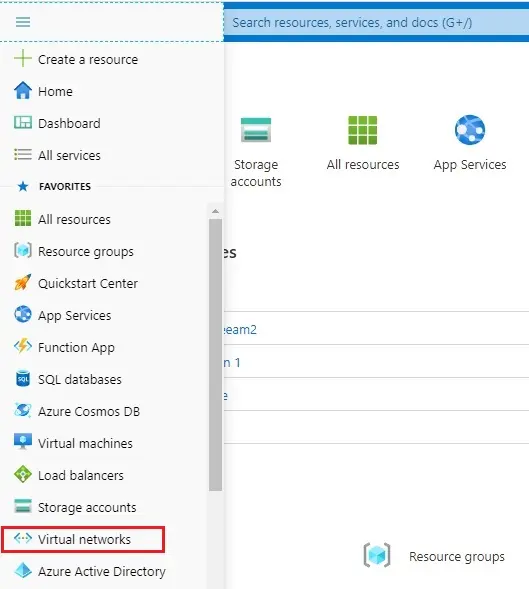
2- In the virtual network, select the add button create a virtual network.
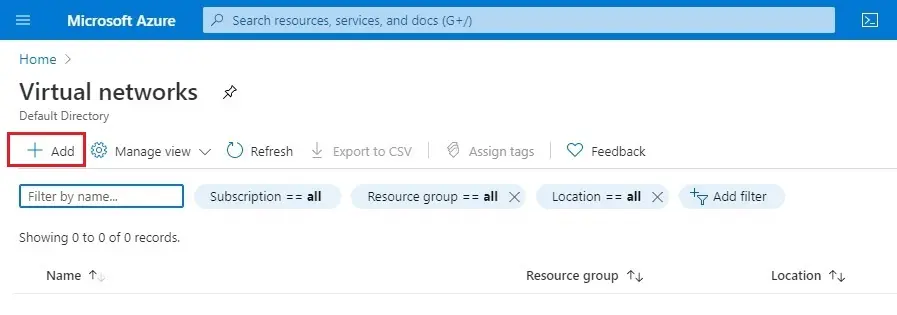
3- Create virtual network window, choose your subscription. Resource Group, select create new to create.
Enter a resource group name (rg-vnet) and then click ok.
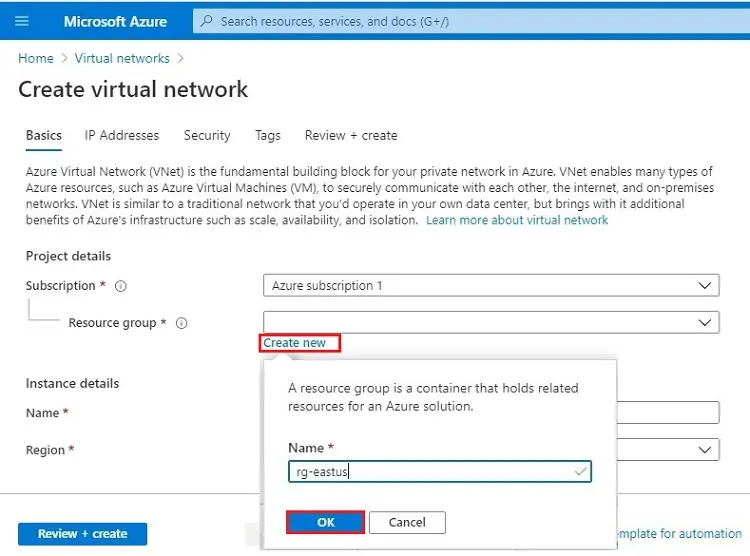
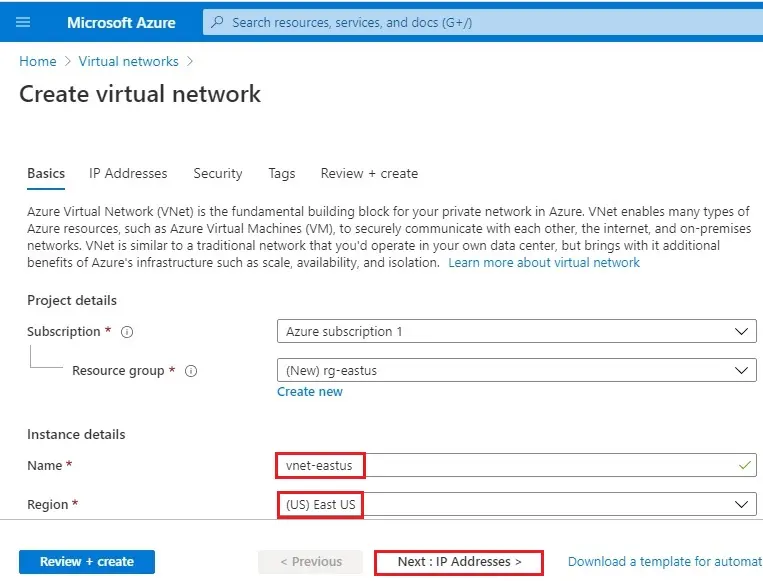
4- Under the instant details type a virtual network name (vnet01).
Choose a location to use as the basis for your virtual network. Select a location that is near to your location to increase performance. Click on Next: IP Addresses >
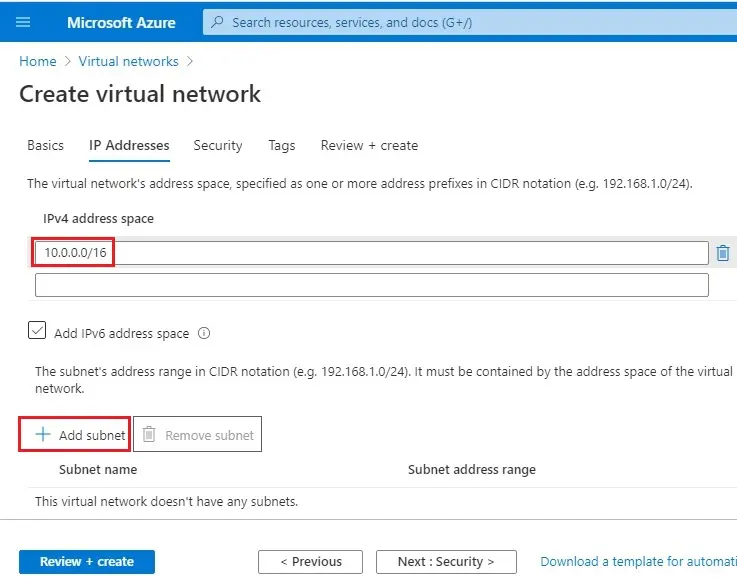
5- Choose an address space IPv4 address space, I am selecting 10.1.0.0/8, but if you prefer to use a different address feels free. Click + Add subnet
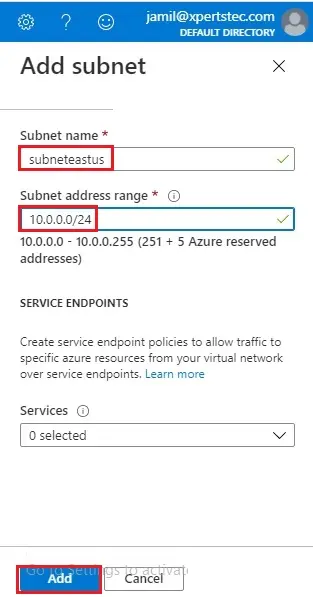
6- In the Add subnet wizard, type a subnet name (vnet-subnet) and then type 10.1.0.0/24 for Subnet address range.
To create service endpoint policy to allow traffic then select a service under services.
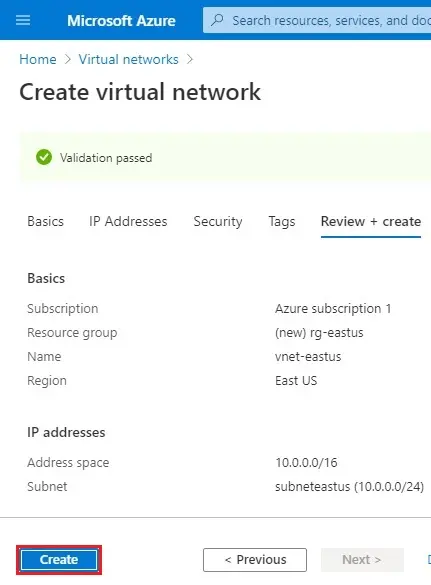
7- Click Next : Review + Create >
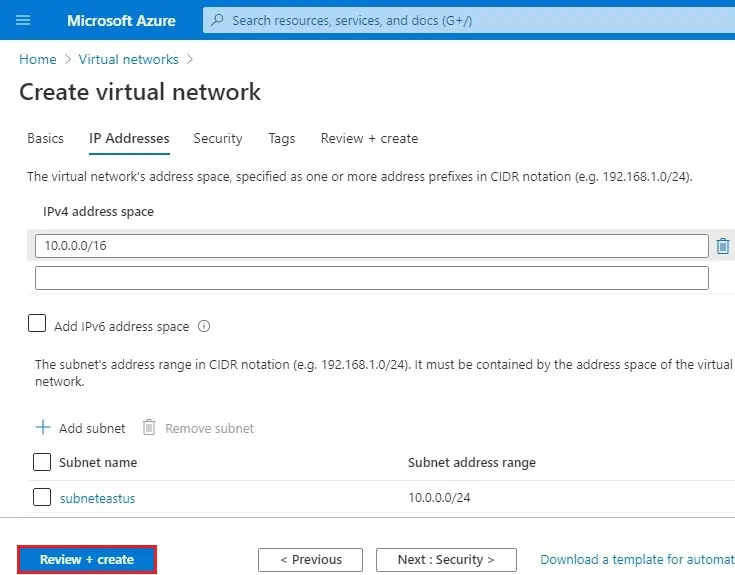
8- Virtual network validation passed, selects Create.
9- To create a 2nd virtual network follow the above steps from 3 to 6 again with the following changes.
| Setting | Value |
| Resources Group | rg-westus |
| Name | vnet-westus |
| Region | (US) west US |
| IPv4 address space | 192.168.0.0/16 |
| Subnet name | subnetwestus |
| Subnet address range | 192.168.1.0/24 |
| Create |
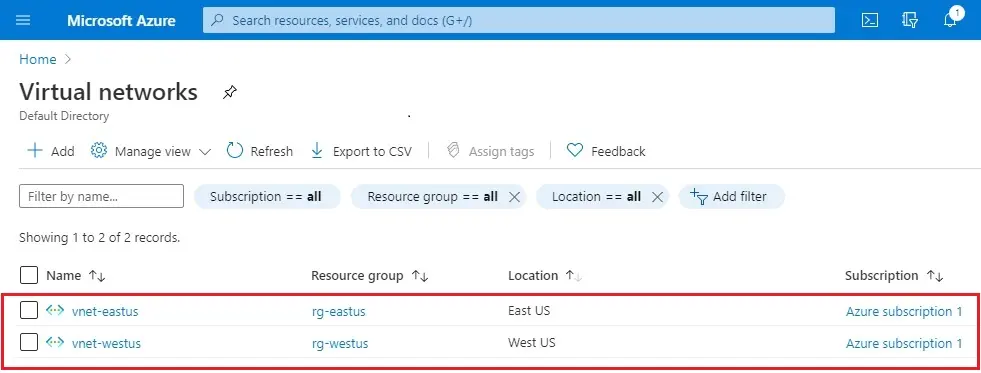
9- Virtual network overview.
Create Virtual Machines
Now we need to create VM in each virtual network so that we can communicate between them.
1st VM
1- Azure portal menu tab, select Virtual Machines.
2- Select the + Add button to create virtual machine.
3- Resource group select existing (rg-eastus).
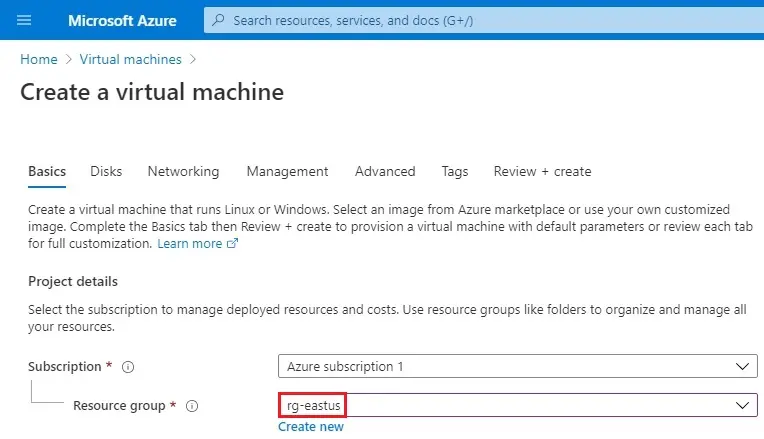
4- Instance details
Enter a virtual machine name (server-eastus)
Region select (East US)
Image selects Windows Server 2019 Datacenter. You can select a different operating system, but the remaining steps presume you selected Windows Server 2019 Datacenter.
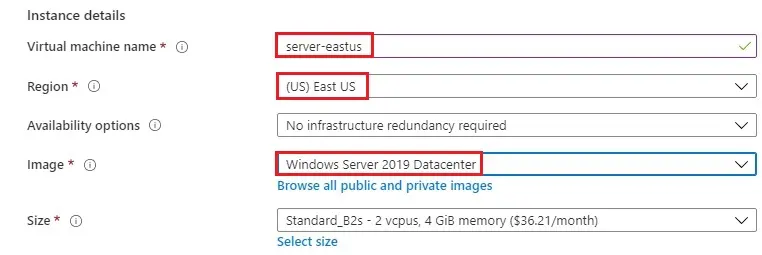
5- Administrator account.
Enter a username (jamil), Password.
Public inbound ports choose allow selected ports.
Select inbound ports (HTTP, RDP) and then click Next : create >
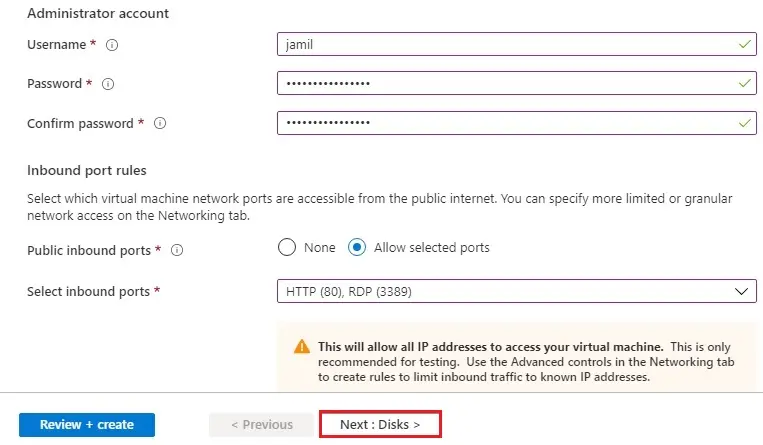
6- Under Management tab
Monitoring boot diagnostics (off) and then click Review + create
7- Select create
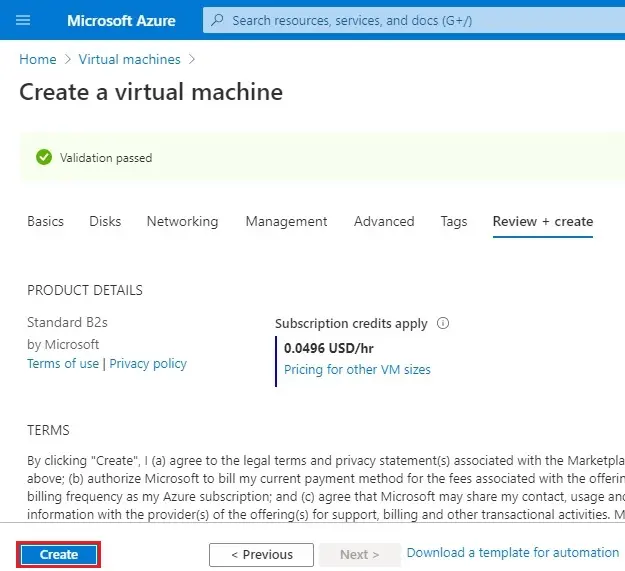
Create the second VM
Complete steps 2 to 7 again with the following changes:-
| Name | Value |
| Resource group | rg-westus |
| Virtual machine name | server-westus |
| Region | (US) West US |
| Image | Windows Server 2019 Datacenter |
| Administrator account | username password |
| Public inbound port | allow selected ports |
| Select inbound ports | HTTP, RDP |
| Management tab | monitoring boot diagnostic (off) |
| Review + create | |
| Create |
The VMs take a few minutes to create. Now the both VMs (web1, web2) successfully created.
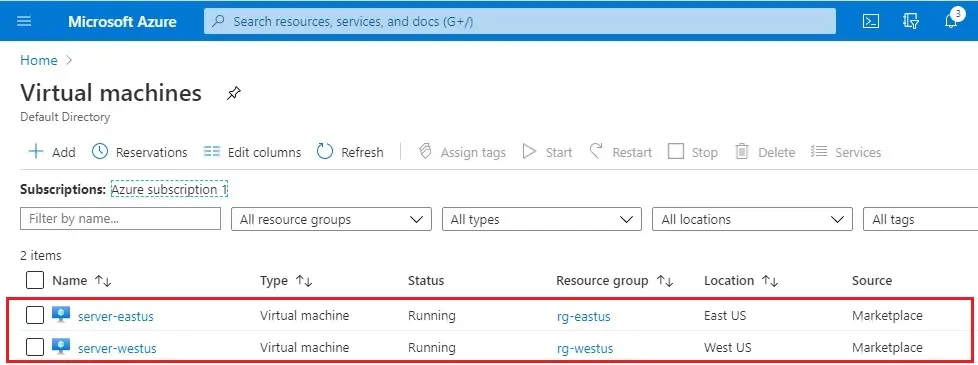
Configure DNS names for the VMs running IIS
In this section, we will configure the DNS names for the IIS servers – server-eastus and server-westus.
1- Select server-eastus
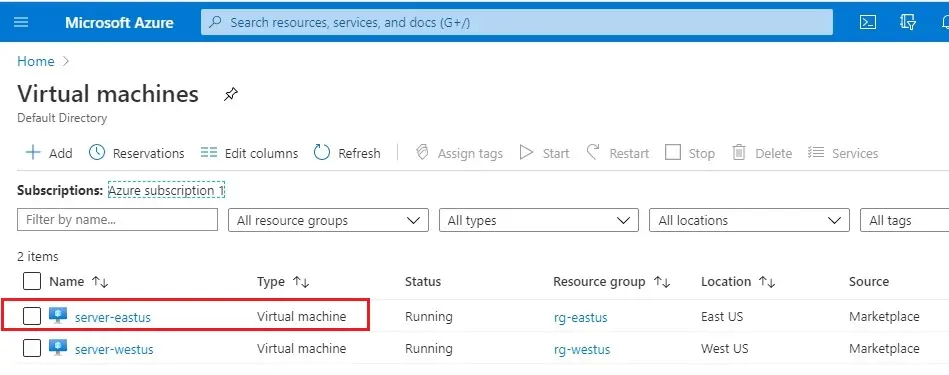
2- Overview page, under DNS name, select Configure.
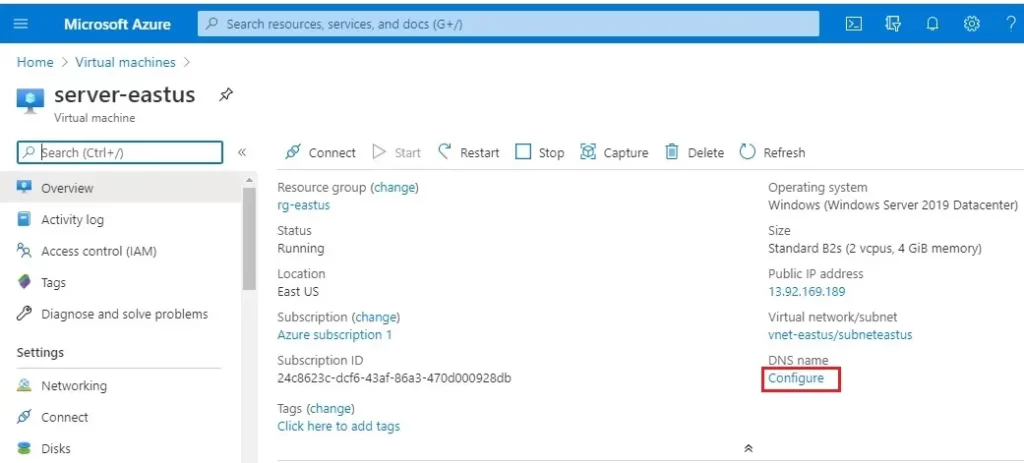
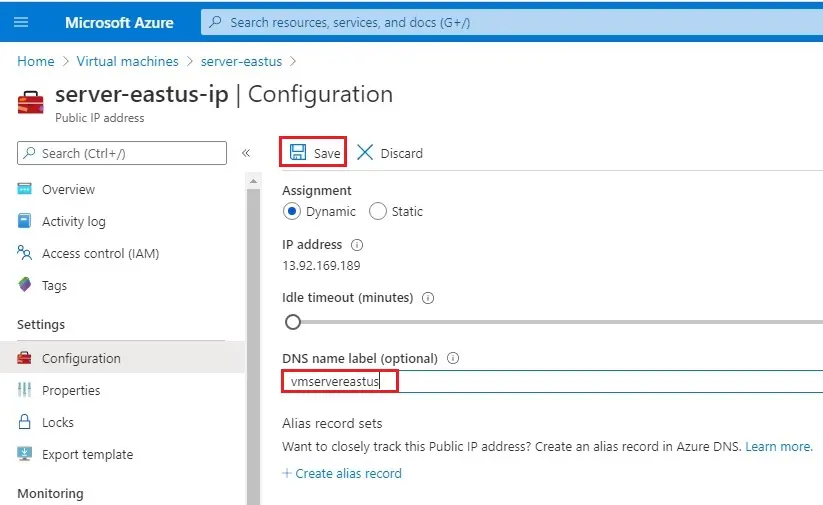
3- Select Configuration under settings, under DNS name label (optional), enter a unique name, and then select Save.
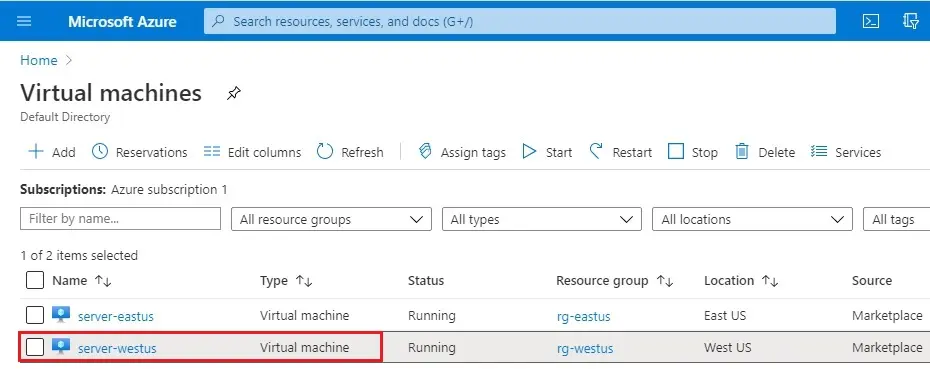
4- Select server-westus.
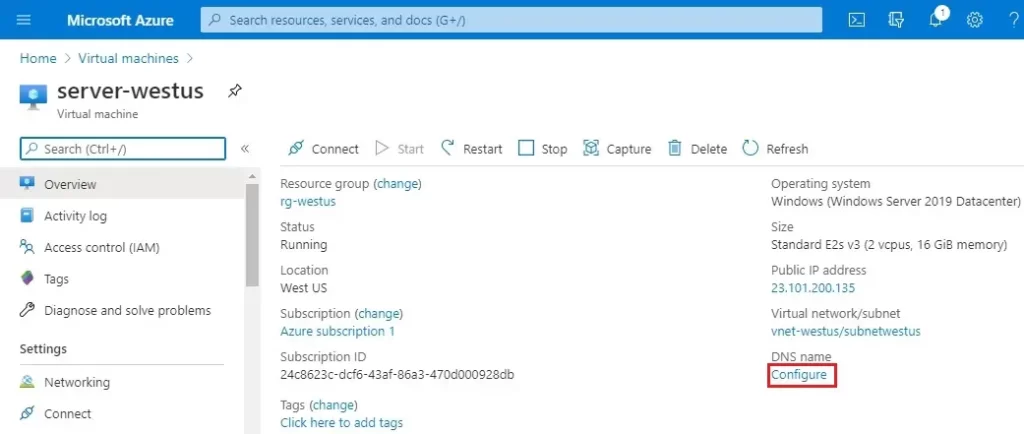
5- On the overview page, under DNS name, select Configure.
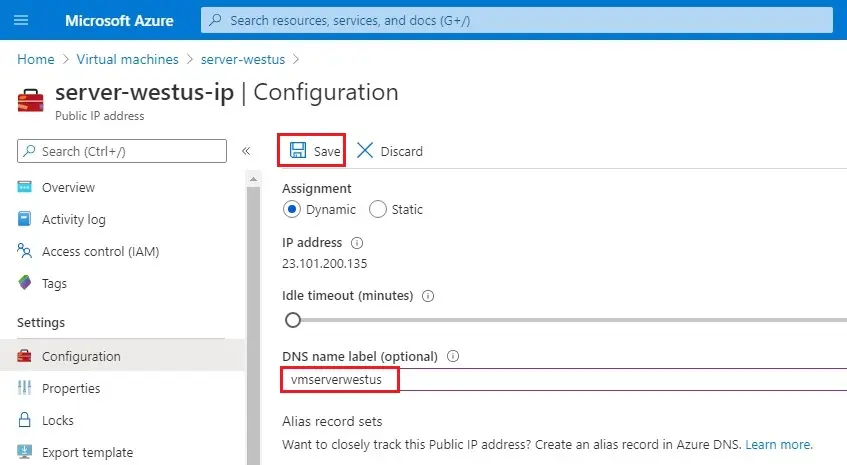
6- Configuration page, under the DNS name label (optional), type a unique name and then select Save.
Create Test VMs
In this section, you create a VM (vmtest-eastus and vmtest-westus) in each Azure region (East US and West US). We will use these VMs (Virtual Machines) to test how Traffic Manager routes traffic to the nearest IIS server when we browse to the website.
1- On the upper left corner of the Azure portal, select the Azure menu and then select the virtual machine.
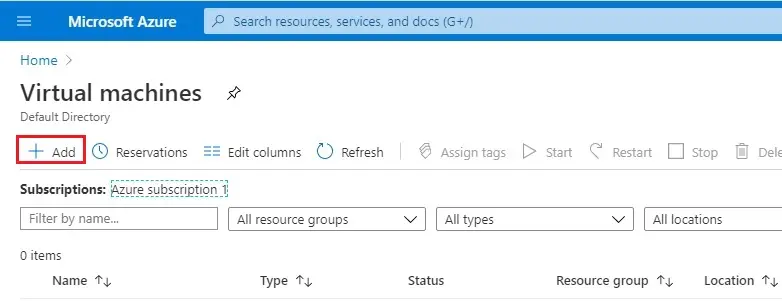
2- In Create a virtual machine, click on + add button.
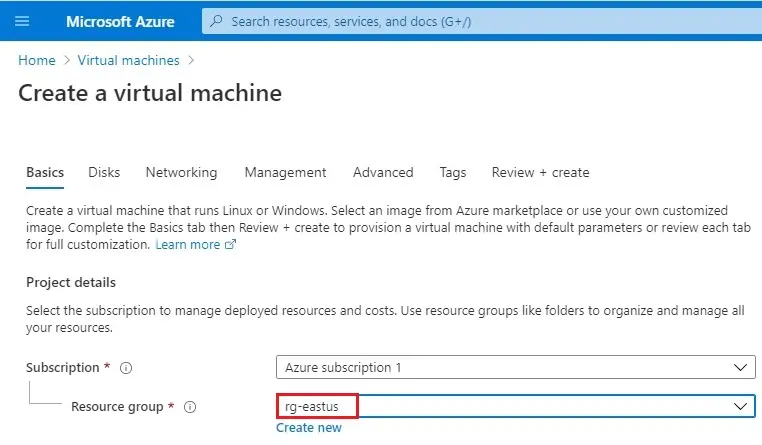
3- In the Basics tab
Select Subscription
Resource Group – Select rg-eastus.
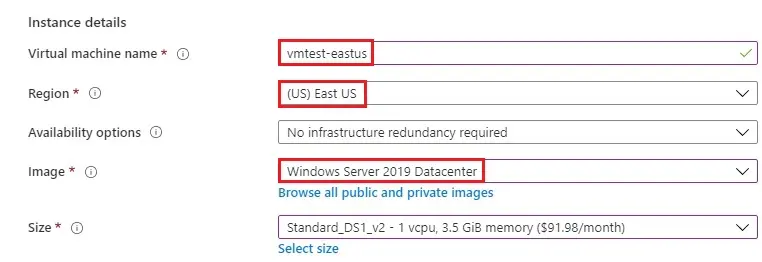
4- Instance Details
Virtual machine name – Type vmtest-eastus.
Region – Select East US.
Image – Windows Server 2019 Datacenter.
5- Administrator Account
Username – Enter a user name.
Password – Enter a password.
Public inbound ports – Choose Allow selected ports.
Select inbound ports – Choose HTTP, RDP in the pull down box.
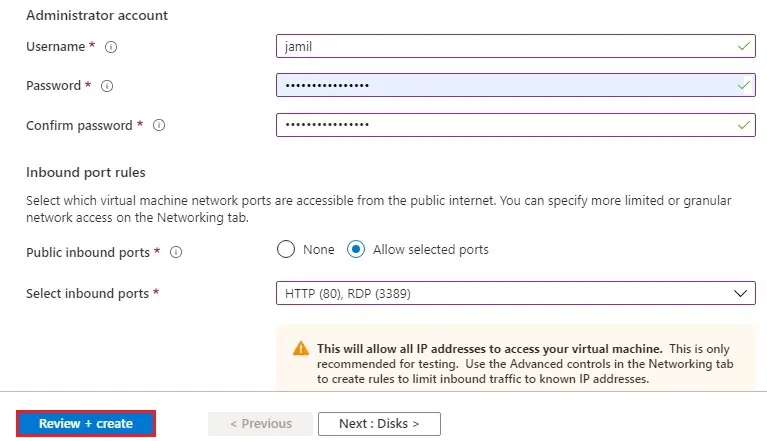
6- Review the settings, and then click Create.
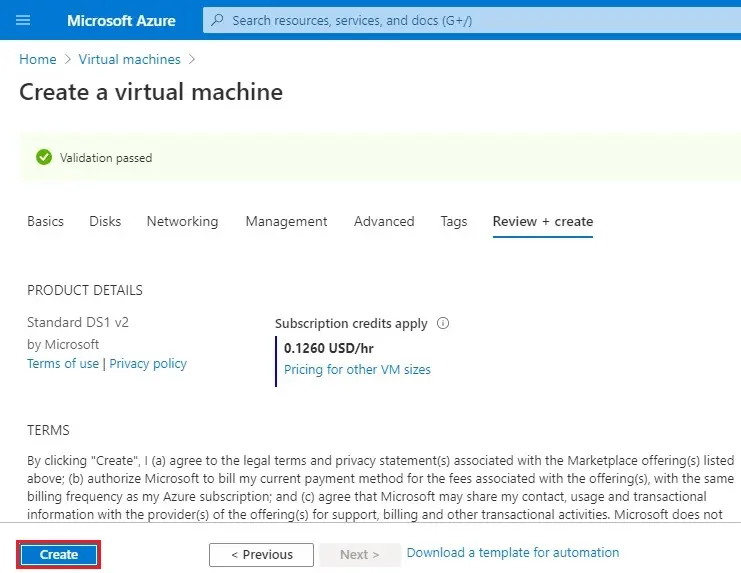
Follow the Steps to Create a 2nd VM.
| Settings | Value |
| Resource group | rg-westus |
| Name | vmtest-westus |
| Region | West US |
| Server | Windows server 2019 datacenter |
| Administrator account | Username, password |
| Public Inbound ports | HTTP, RDP |
| Review + create | |
| create |
The VMs take a few minutes to create. Please do not continue with the remaining steps until all VMs are created.
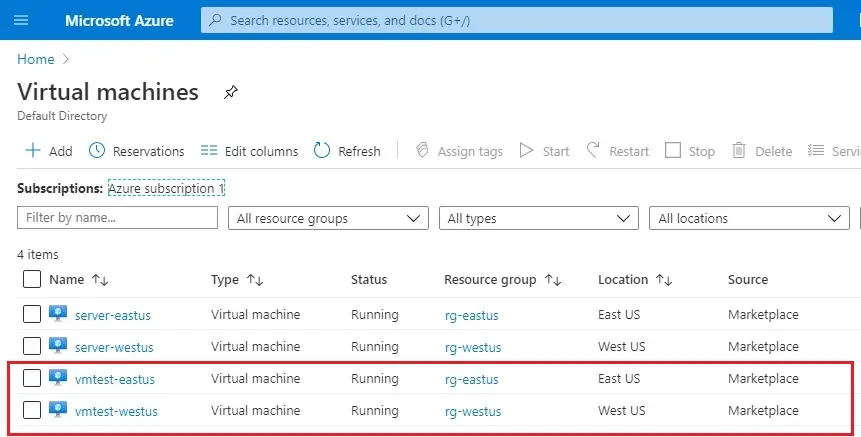
Create a Traffic Manager profile
To create a Traffic Manager profile that instructs user traffic by sending them to the endpoint with the lowest latency.
1- In the Azure search type traffic manager, select Traffic Manager Profiles.
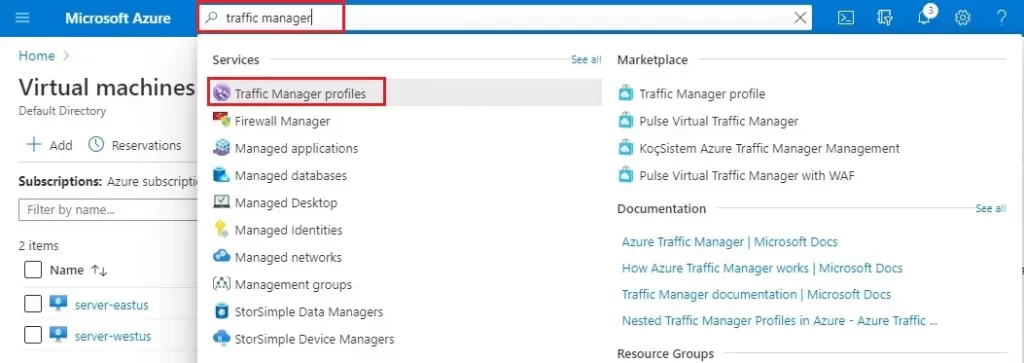
2- Traffic Manager profiles, click the + Add.
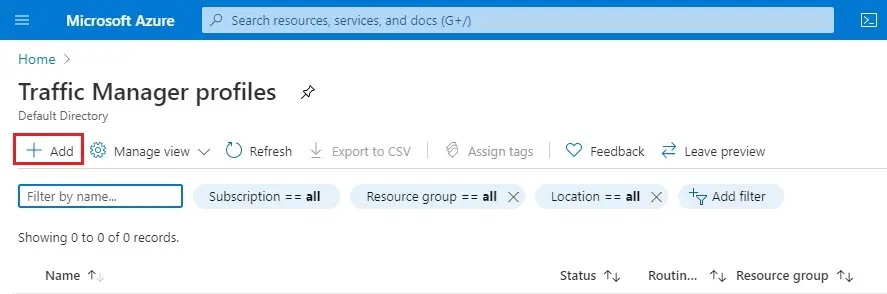
3- In the Create Traffic Manager profile wizard
Name – Type a name (trafficmanager33)
Routing method – type Performance
Select Subscriptions
Resource group – select rg-eastus
Select Create
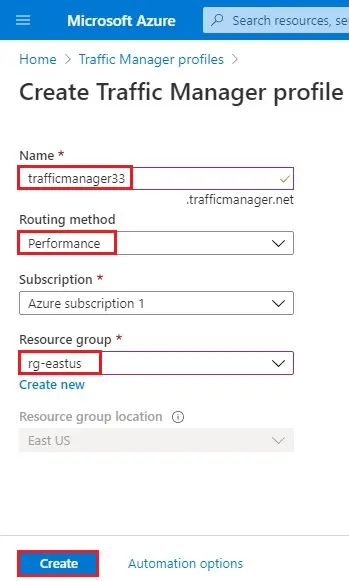
4- Traffic Manager profiles.
Add Traffic Manager Endpoints
Add the two VMs running the IIS servers – server-eastus & server-eastus- to route user traffic to the endpoint closest to the user.
1- In the portal’s search bar, search for the Traffic Manager profile and then select it.
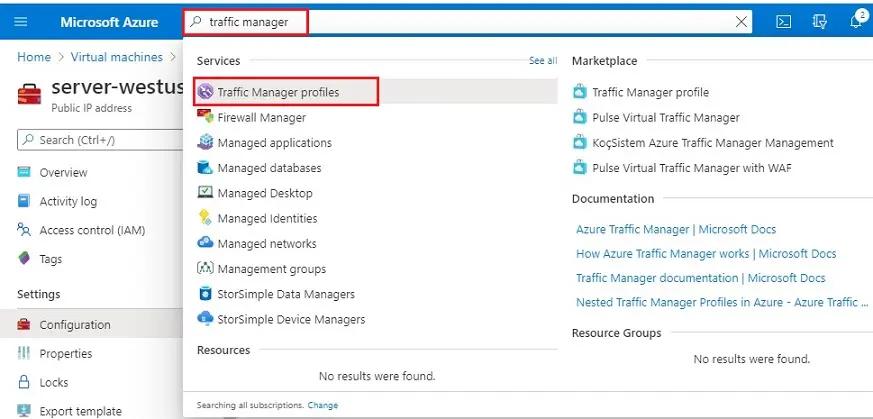
2- In Traffic Manager profile, click on trafficmanager33.
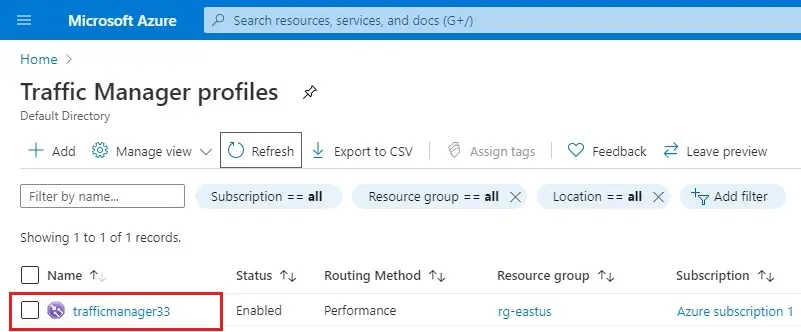
3- Select Endpoints under settings, and then click + Add.
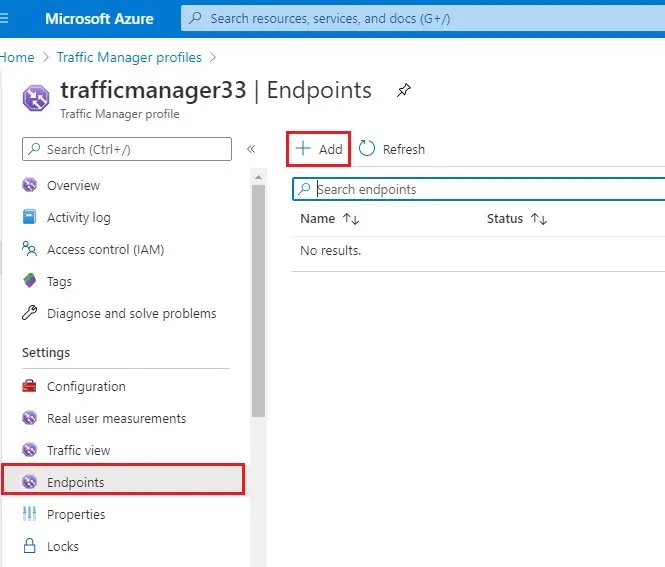
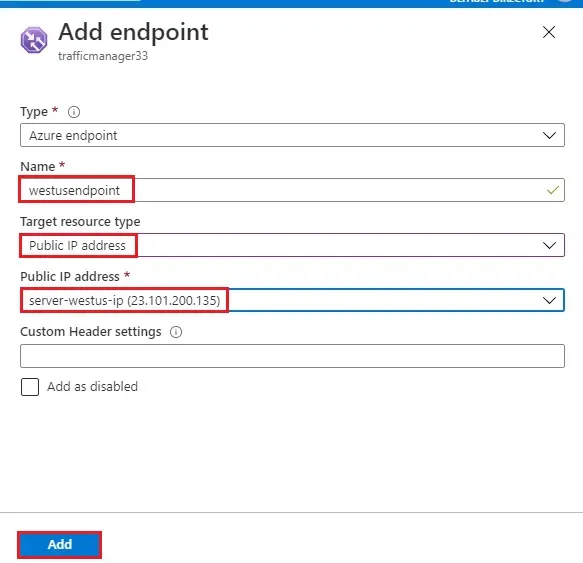
4- Add Endpoint
Type – Azure endpoint
Name – eastusendpoint
Target Resource type – Public IP address
Public IP address – server-eastus-ip
Click Add
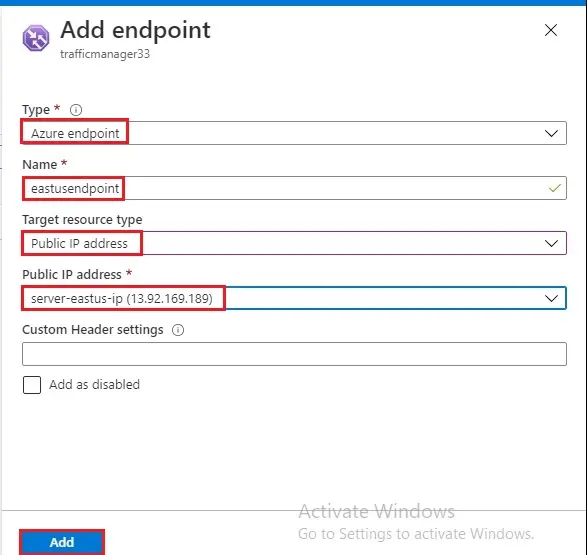
5- Select + add button again for second endpoint.
6- Add Endpoint
Type – Azure endpoint
Name – westusendpoint
Target Resource type – Public IP address
Public IP address – server-westus-ip
Click Add
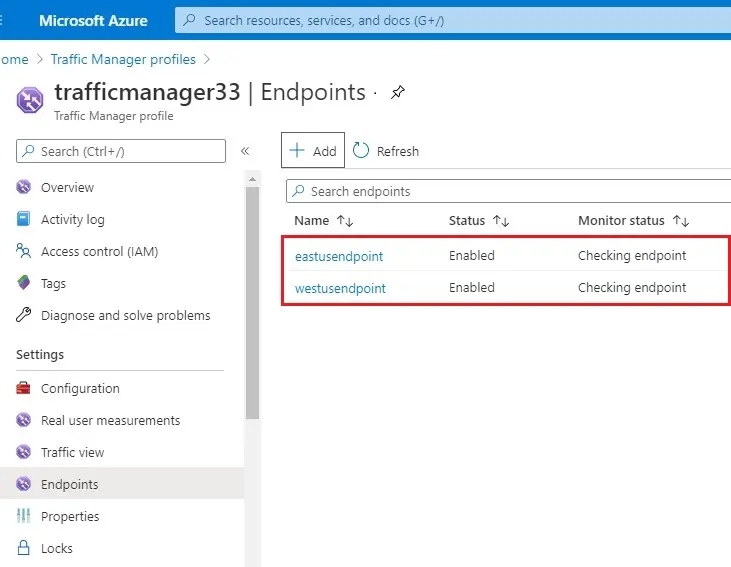
7- After the addition of both endpoints completed, they will displayed in Traffic Manager Profile together with their monitoring status as Online.
Test Traffic Manager Profile
Determine DNS name of Traffic Manager Profile
In this step, we use the DNS name of the Traffic Manager profile to visit the websites.
1- In the Azure search bar, search for the Traffic Manager profile name and then select it that we created in the preceding section. select the traffic manager profile.
Overview
2- Your Traffic Manager profile will display the DNS name of your newly created one.
Copy DNS name
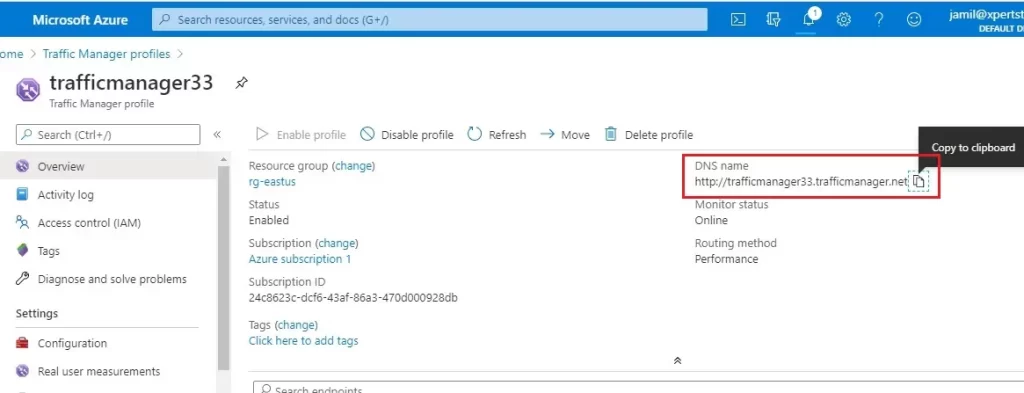
Improve Website Response using Traffic Manager
3- Go to the virtual machines and then click vmtest-eastus.
4- Connect virtual machine (server-eastus), using RDP.
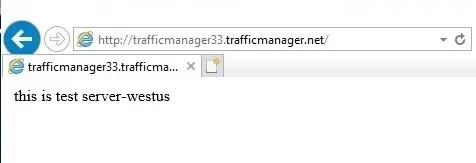
5- Open web browser on the VM (instance) vmtest-eastus, enter the DNS name of the Traffic Manager profile to view the website. Since the VM located in East US, you are routed to the nearest website hosted on the nearest IIS server server-eastus that is located in East US.
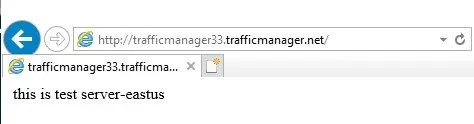
6- Connect virtual machine (server-westus), using RDP
7- Open web browser on the VM vmtest-westus, type the DNS name of your Traffic Manager profile to view your website. Since the VM located in West US, you are routed to the nearest website hosted on the nearest IIS server server-eastus that is located in West US.