This blog has detailed how to schedule Windows Server Reboot Automatically (Windows or Server 2008/2019). You may want to reboot a Windows Server once a week or month as a matter of routine maintenance. It’s particularly useful too. Say you want to reboot a server because you installed particular software that you didn’t expect needed a restart, or there are some updates. You cannot really do it unless after hours and you don’t need to hang around and then you would just like it to reboot itself a couple of hours after working hours when everyone left.
Note: I’m using Windows Server 2019. This is almost the same as in 2008/2012/0216.
Read also: How to Create Scheduled Task in Windows 10
Schedule Windows Server Reboot Automatically
1- Select the search bar and type Task Scheduler, click on it to open. You can find it by clicking on the Windows start button, expanding Windows Administrator Tools, open Control Panel to select Administrative Tools.
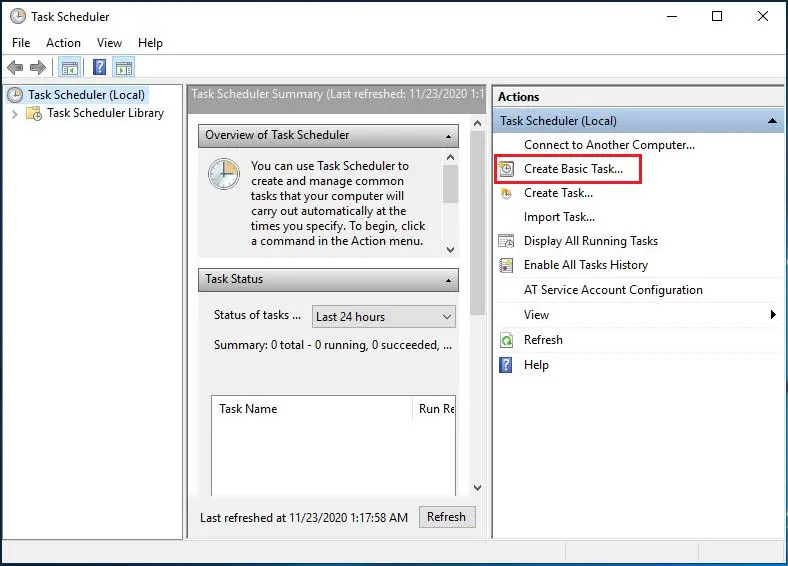
2- Create a new basic task using the Create Task action.
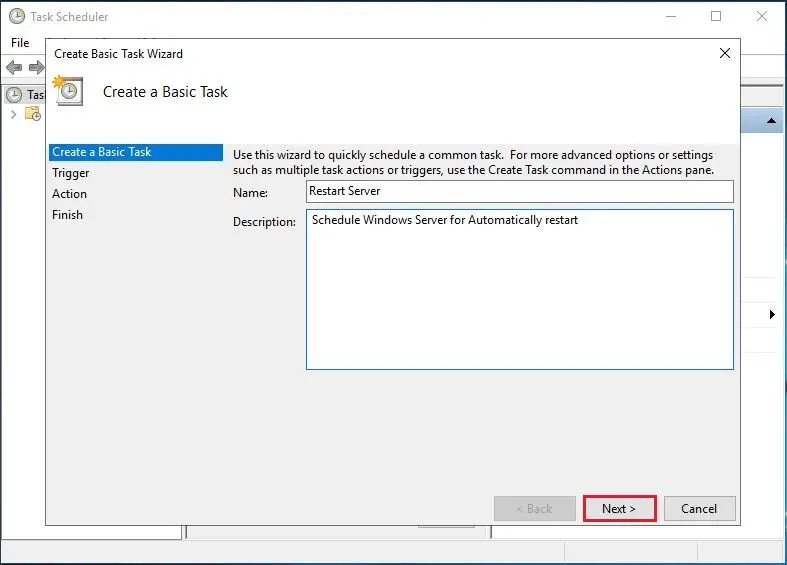
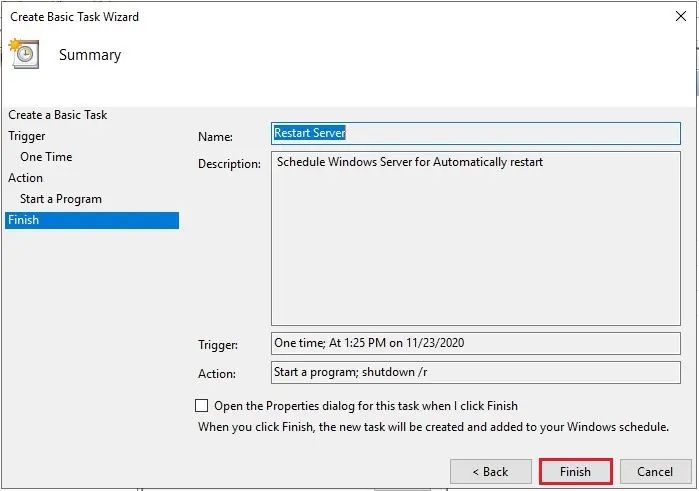
3- Type a name for the task. I renamed it Restart Server or (Restart This Server). Type a description Schedule Windows Server for Automatically restart.
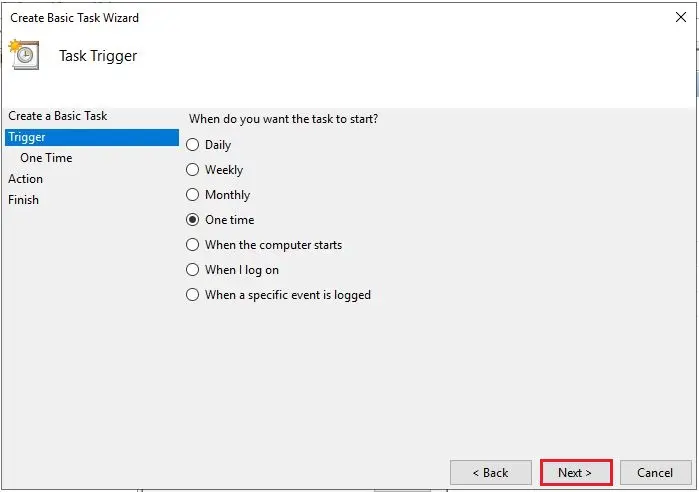
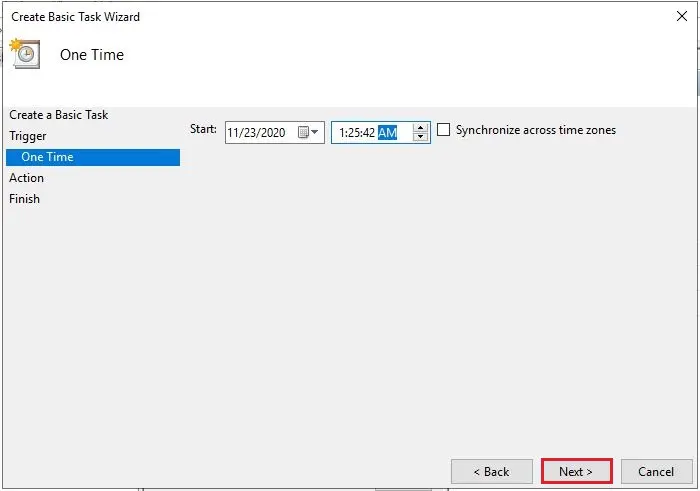
4- Since this task is to just restart the server one time (select one time) and then click next.
5- Provide it a date and time to restart. Click next.
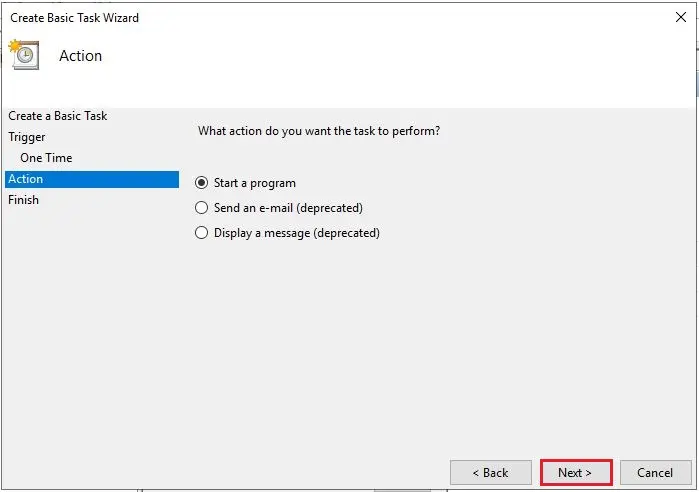
6- Select Start A Program action and then click Next.
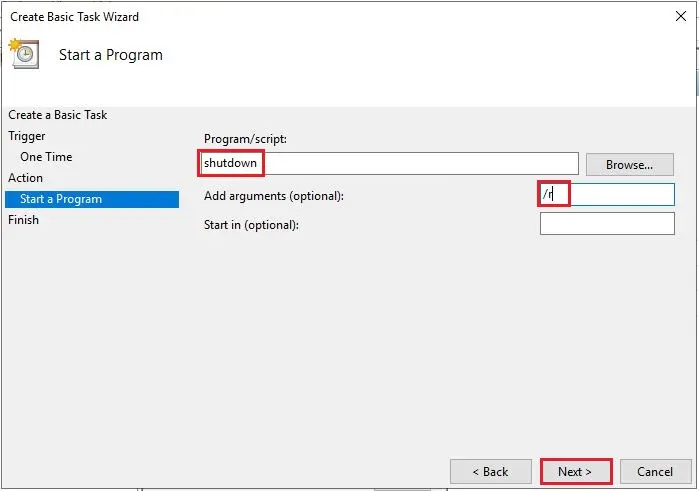
7- Type shutdown into the Program/Script box and then /r into the Add arguments box. Click Next.
8- Click Finish.
9- We are almost done if you want this to run if you get logged off and you want to set this up so you can use it again later. In the Task Scheduler right-click on your new task and then select Properties.
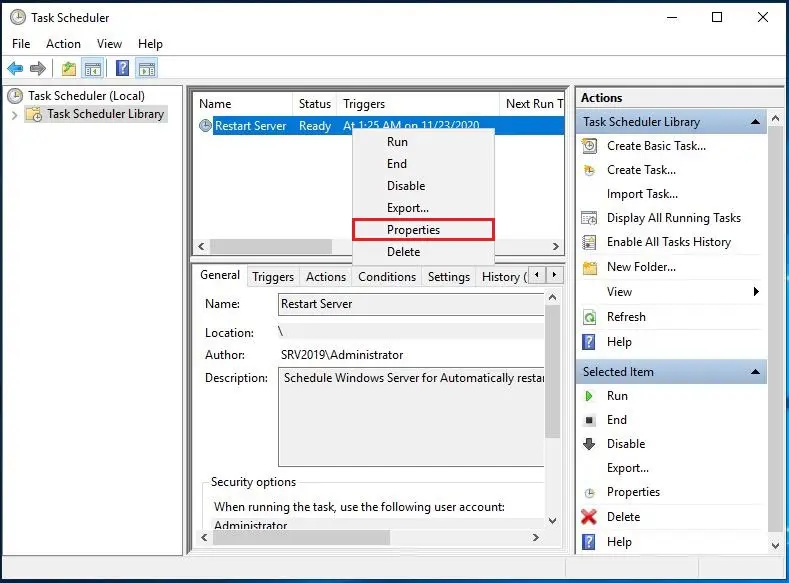
10- This will show up on the general settings page. The default settings are “Run only when the user is logged on” Switch it to “Run whether the user is logged on or not”. Choose Configure to select the Server you want to reboot.
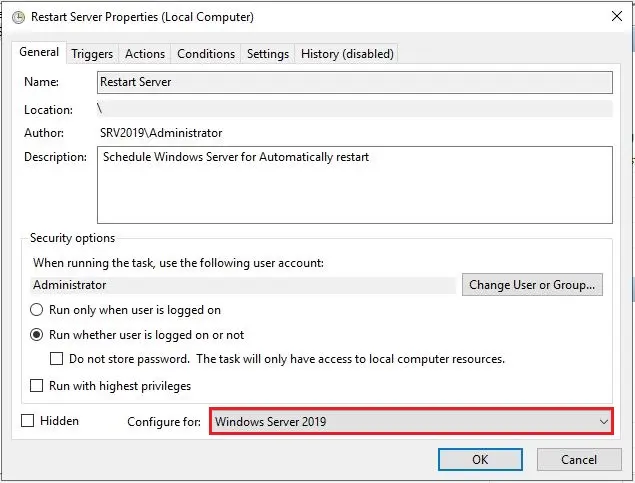
11- Select ok, after typing your administrator password.
Changing the Schedule for The Automatic Reboot
So now we have a task that will automatically reboot our Windows server (Computer, PC) one time.
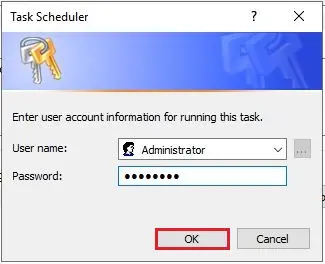
12- Go back to the Task Scheduler Window, right-click on the task, and then click Properties. Select the Triggers tab.
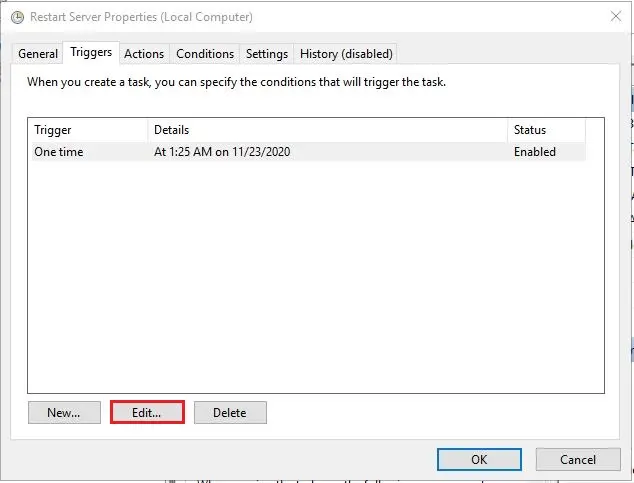
13- Select the One Time trigger and then click the Edit button. Change the time and date, click ok and your server/PC/computer will now restart at the new time.
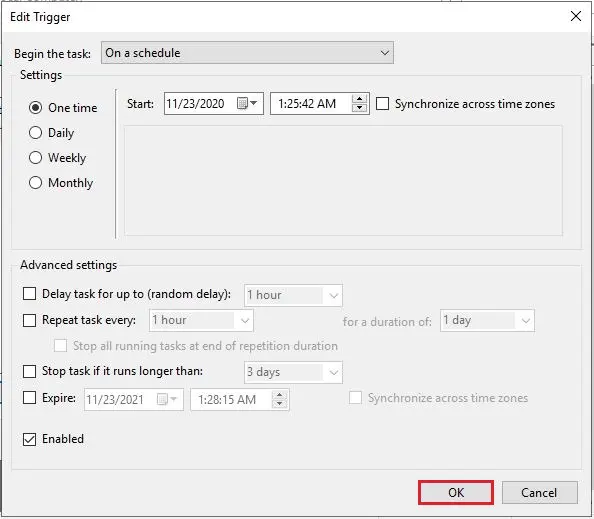
14- When you click ok it will ask you to re-enter the administrator password.
Watch Video: How to schedule Windows Server reboot automatically.
FAQs
What is the most effective way to plan Windows Server’s automatic reboots?
The Task Scheduler function integrated into Windows Server is the best way to arrange automatic reboots. You can build scheduled tasks in Task Scheduler that can start a server reboot at predetermined intervals or particular days and hours. You can automate the reboot procedure without any human intervention by specifying the proper parameters in Task Scheduler. This guarantees that your Windows Server reboots on a regular basis, enhancing system performance and health.
How can I restart Windows Servers in a program for routine maintenance?
To automate Windows Server reboots for routine maintenance, utilize Task Scheduler. By creating a scheduled job in the work Scheduler, you can set the ideal timing and frequency for the automated reboots.
You can configure it such that the server reboots either once a week or once a month, depending on your maintenance requirements. Now that human interaction is no longer necessary, you can focus on other important tasks while still making sure that your Windows Server reboots periodically for peak performance.
What are the benefits of scheduling Windows Server reboots automatically?
Scheduling Windows Server reboots automatically offers several benefits, including:
Streamlined maintenance:
Automated reboots ensure routine maintenance tasks, such as installing updates or software, are performed on schedule, reducing the risk of neglecting important tasks.
Time savings:
By eliminating the need for manual intervention, administrators can save time and effort that would otherwise be spent initiating reboots individually.
Increased productivity:
Scheduled reboots can be set to occur during off-peak hours or after work hours, minimizing disruptions to users and maximizing productivity.
Improved stability:
Regular reboots help refresh system resources, clear memory, and resolve certain software or configuration issues, leading to improved server stability and performance.
By scheduling Windows Server reboots automatically, you can ensure that your server operates at its best while minimizing manual effort and interruptions.
Can I schedule specific dates and times for Windows Server automatic reboots?
Yes, you can schedule specific dates and times for Windows Server automatic reboots using Task Scheduler. You can set the trigger parameters when creating a task in Task Scheduler to specify the precise date, time, and repetition pattern for the automated reboot. With this flexibility, you can modify the schedule to suit your requirements and make sure that the server reboots when you want it to without the need for user intervention.
Are there any risks or considerations when scheduling automatic reboots for Windows Server?
When scheduling automatic reboots for Windows Server, there are a few risks and considerations to keep in mind:
Impact on running processes:
Rebooting the server automatically may interrupt running processes or services, potentially affecting ongoing operations. It is important to plan the reboot schedule carefully to minimize disruptions.
Data loss or corruption:
Before starting automated reboots, make sure that all unsaved data is correctly saved and backed up to avoid any possible data loss or corruption.
Application compatibility:
Prior to setting up automatic reboots, it’s important to take into account any requirements or dependencies that some apps or services may have. To prevent any problems, make sure that crucial apps are compatible with the reboot schedule.
Compatibility with applications:
Some applications or services may have specific requirements or dependencies that need to be considered before scheduling automatic reboots. Ensure that critical applications are compatible with the reboot schedule to avoid any issues.
By considering these risks and taking appropriate measures, such as proper data backup and compatibility checks, you can mitigate potential issues and ensure the smooth execution of scheduled Windows Server reboots.
How to ensure the successful execution of scheduled Windows Server reboots?
To ensure the successful execution of scheduled Windows Server reboots, consider the following tips:
Test the reboot process:
Before implementing the scheduled reboot, test the process on a non-production environment to ensure it works as intended.
Monitor system health:
Regularly monitor the server’s health and performance to identify any potential issues that may impact the scheduled reboots.
Check for pending updates:
Ensure that all pending updates are installed before initiating the reboot to prevent conflicts or incomplete installations.
Communicate with users:
Inform users or stakeholders about the scheduled reboots to minimize any potential disruptions and ensure they are aware of the maintenance schedule.
By following these guidelines, you can increase the likelihood of successful execution and minimize any potential issues during scheduled Windows Server reboots.
Is it possible to schedule Windows Server reboots for after-hours to minimize disruption?
Yes, it is possible to schedule Windows Server reboots for after-hours to minimize disruption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this guide has provided a comprehensive explanation of how to schedule Windows Server reboot automatically, specifically for Windows Server 2008/2012/2016/2019. Regular server reboots are essential for routine maintenance, and this automated scheduling process proves to be highly beneficial.
Whether it’s for unexpected software installations requiring a restart or system updates, automating the reboot process allows for convenient execution during after-hours when staff is not present.


