This article will teach you how to access Windows 11 advanced startup options. Advanced Startup Options in Windows 11 allows you to restore your operating system or troubleshoot when there are issues you can’t fix from within the operating system. Advanced Startup Options is not something we need to access often but is indispensable when needed. I read a recent blog post where the author stated that Advanced Startups can be hard to find. There are multiple ways to access Advanced Startup, most of which are simple.
Booting Into Advanced Startup in Windows 11
These methods are provided so that you can access the desktop. The most effective method is to hold down the Shift key while clicking Restart.
Access Windows 11 Advanced Startup Options Via Settings
Right-click on the Windows start button and click on settings.
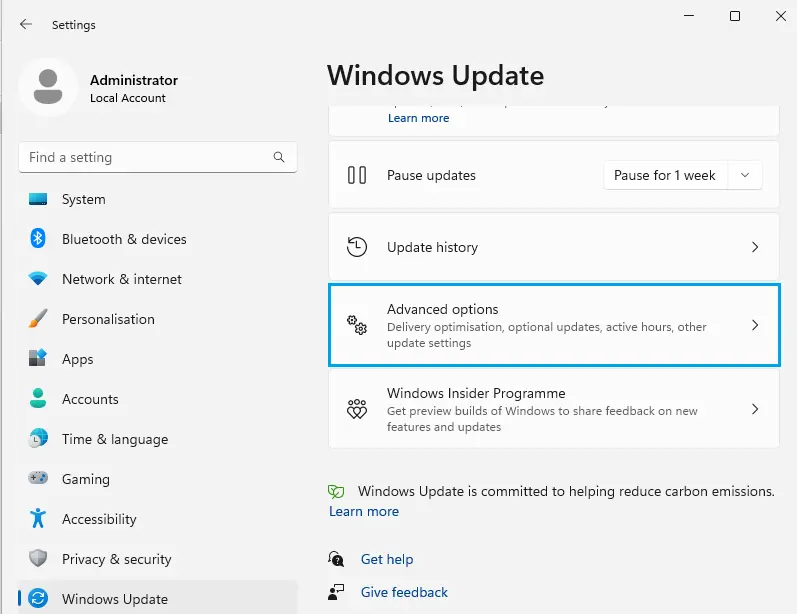
Click on Windows updates and click on advanced options.
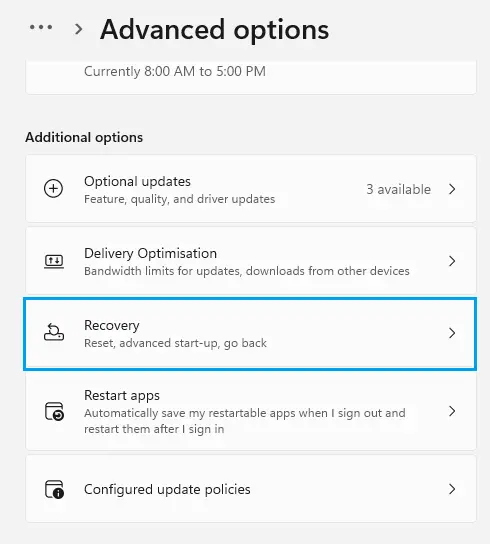
In the advanced options, click on Recovery.
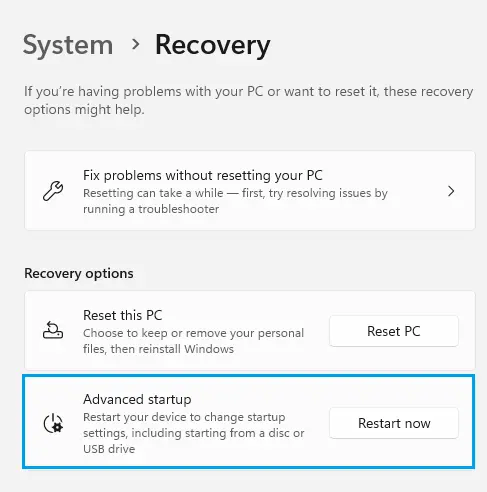
Under the Advanced Startup, select the Restart Now button.
Access Windows 11 Advanced Startup Options Via Shift Key + Restart
Right-click on the Start button (or Windows key + X)
Hover the mouse cursor over Shut down or sign out, hold down the Shift key for a while, and click Restart.
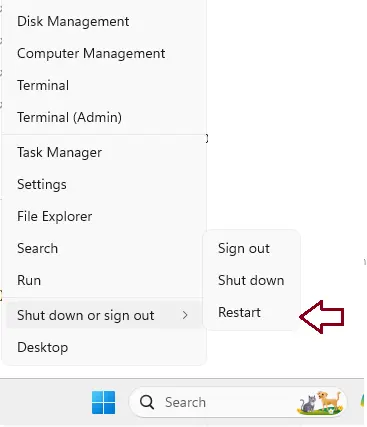
To access the Advanced Startup Options menu, click Troubleshoot and Advanced Options.

Create Desktop Shortcut to Access Windows 11 Advanced Startup Options
As mentioned above, accessing Advanced Startup is not something users need to do frequently, so you would be in serious trouble if that were the case. As a result, creating a desktop shortcut is unnecessary, particularly considering the easy alternatives. Though, as for a bit of fun and perhaps a learning curve, here is how to create a desktop shortcut:
Right-click any blank space on your desktop, choose New and then Shortcut.
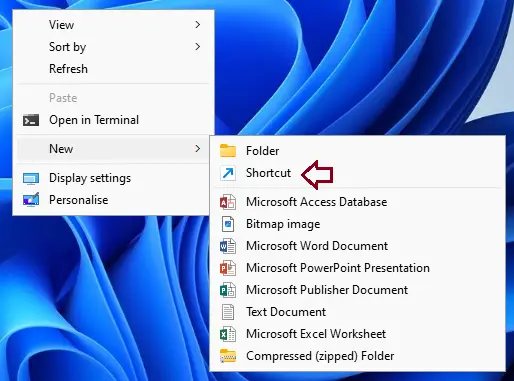
Type in (or copy and paste the below)
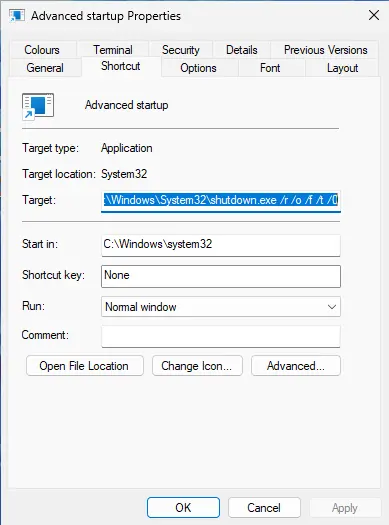
shutdown.exe /r /o /f /t 0
Click next.
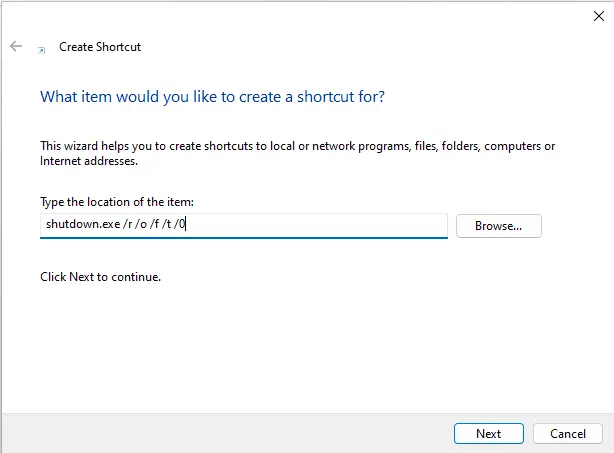
The default address is shutdown.exe. You can change it to anything you wish (Advanced Startup) and click Finish.
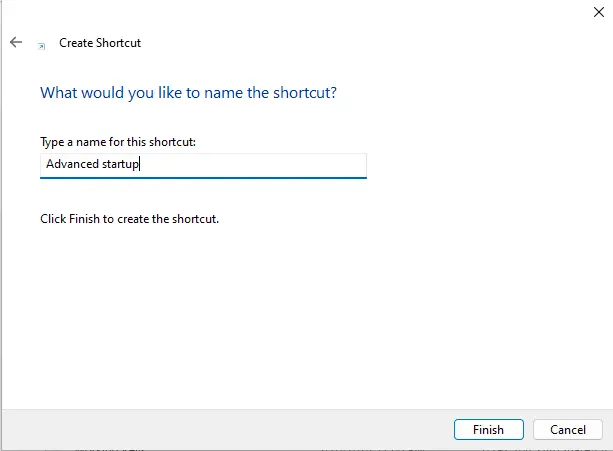
To associate an icon with the new shortcut, right-click on the shortcut and choose Properties.
Click the Change Icon.
Please visit Microsoft to learn more about advanced startup options.


